Table Of Content
- It cannot be used to analyze behavior over a period of time
- Strengths of a Cross-sectional Study
- thought on “Cross-Sectional Study- Definition, Types, Applications, Advantages, Limitations”
- Cross-Sectional Studies: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Recommendations
- Table 1:
- What’s the difference between cross-sectional and cohort studies?
The survey was conducted by the nursing department, and it included a total of 3,450 nurses who were employed at the hospital. In the end, a grand total of 2,811 individuals supplied valid and useful responses, leading to an effective response rate of 81.49%. An ensemble of web-based surveys that individuals completed themselves was utilized. Participants successfully filled out a well-organized questionnaire within a time frame of 20 to 25 min. Figure 1 provides a visual representation of the specific information using a flow chart. 3) The relationship between simulation educational satisfaction, simulation design, and flow was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
It cannot be used to analyze behavior over a period of time
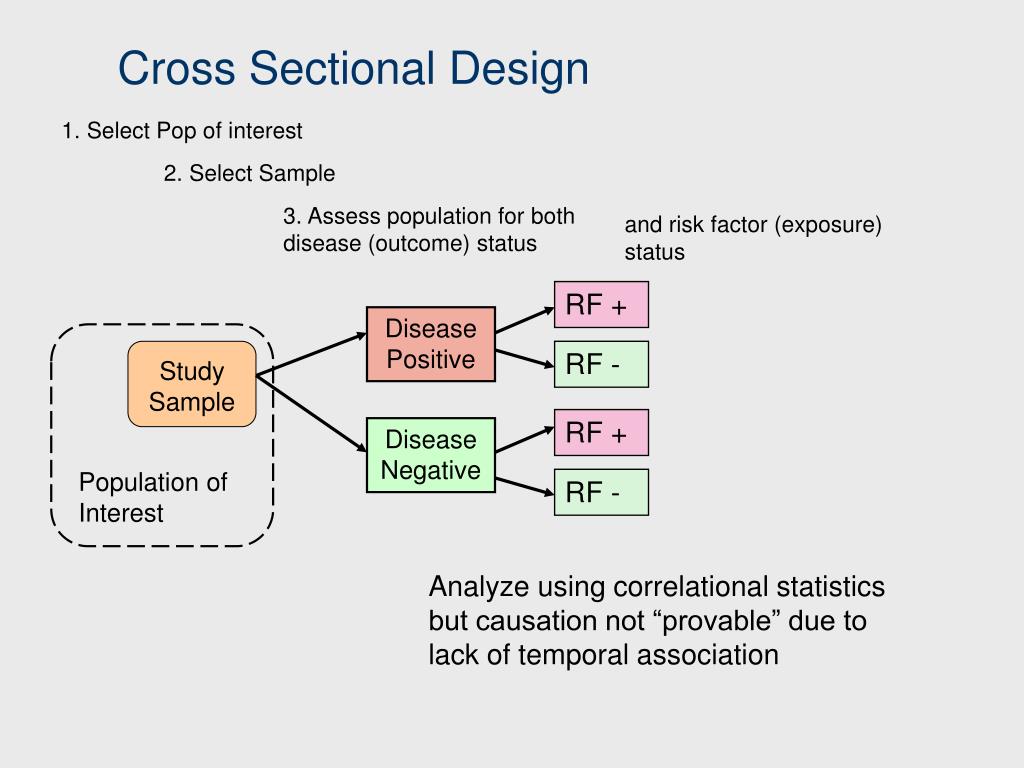
When you want to examine the prevalence of some outcome at a certain moment in time, a cross-sectional study is the best choice. A cross-sectional study is a cheap and easy way to gather initial data and identify correlations that can then be investigated further in a longitudinal study. A reporting guideline for cross-sectional studies is available for investigators and consumers of research to use.
Strengths of a Cross-sectional Study
In a cross-sectional study, data are collected from a sample of the target population at a specific point in time, and everyone in the sample is assessed in the same way. There isn’t a manipulation of variables or a control group as there would be in an experimental study design. A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted from April to November 2019 among individuals living in both private and government MUH complexes in seven divisional cities of Bangladesh.
Insights from a cross-sectional binational study comparing obesity among nonimmigrant Colombians in their home ... - BMC Public Health
Insights from a cross-sectional binational study comparing obesity among nonimmigrant Colombians in their home ....
Posted: Sun, 06 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
thought on “Cross-Sectional Study- Definition, Types, Applications, Advantages, Limitations”
Evidence-based practice includes the integration of best available evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values and circumstances related to patient and client management, practice management, and health policy decision-making. A cross-sectional study does not need to have a control group, as the population studied is not selected based on exposure. Cohort studies, on the other hand, begin by selecting a population of individuals who are already at risk for a specific disease. Unlike cross-sectional studies, researchers can use longitudinal data to detect changes in a population and, over time, establish patterns among subjects. Both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies are observational and do not require any interference or manipulation of the study environment. Researchers are able to look at numerous characteristics (ie, age, gender, ethnicity, and education level) in one study.
Training and data collection
During the debriefing process, learners who participated in the simulation acquire knowledge and skills about the simulation situation and can learn through reflection [7]. Well-designed simulation-based education improves clinical decision-making, promotes learning engagement, and increases satisfaction and confidence in learning [15,16,17]. A cross-sectional study is a type of observational research design that involves collecting data from a group of participants at a single point in time to assess various characteristics or variables of interest.
Cross-Sectional Studies: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Recommendations
Primary outcome measure Multinomial logistic regression was used to identify the determinants of the choice of smoke-free policies for MUH. The data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 for Windows, developed by SPSS Inc. in Chicago, IL, USA. The continuous variables were reported as the median together with the interquartile range. The mean of two continuous variables that follow a normal distribution was compared using the Student's t-test. The Mann–Whitney U test was employed to compare the average values of two continuous variables that do not follow a normal distribution.
Table 1:
A cross-sectional study design is a type of observational study, or descriptive research, that involves analyzing information about a population at a specific point in time. According to the present study’s findings, non-smoking MUH residents were more likely to favour a smoke-free building policy than those who were smokers. The results of multinomial logistic regression analyses are displayed in table 4.
Third, the exclusion of pregnant women and individuals with speech and/or hearing impairments may have biased the study results. Culturally, Bangladeshi women do not go outdoors during pregnancy and experience a sense of embarrassment in conversations with unknown people, especially with adult men. An interviewer-administered survey involves verbal communication between interviewers and respondents, which is challenging for individuals with speech and hearing impairments. Finally, we included only those residents who were available at home during data collection.
What’s the difference between cross-sectional and cohort studies?
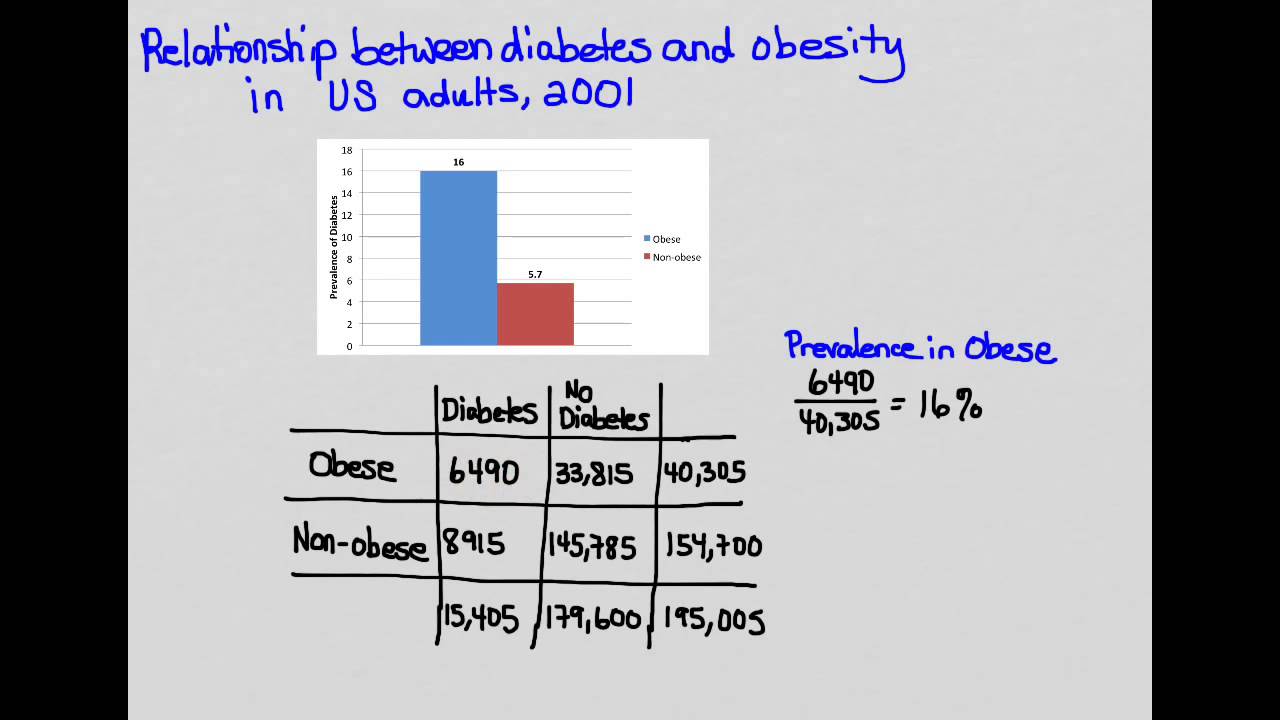
If the RR was less than 1, it implies that the exposure had a protective effect in that obese HIV participants were less likely to be sedentary than the unexposed group (not obese). All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies. Epidemiology is a branch of public health that views a community as the “patient” and various health events as the “condition” that needs treatment, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Case-control studies differ from cross-sectional studies in that case-control studies compare groups retrospectively and cannot be used to calculate relative risk. Cross-sectional studies rely on surveys and questionnaires, which might not result in accurate reporting as there is no way to verify the information presented. These studies are quick, cheap, and easy to conduct as they do not require any follow-up with subjects and can be done through self-report surveys.
To prevent duplicate survey participation, only one response could be submitted per IP, and only one response per item was allowed to exclude multiple responses. The mobile phone numbers collected for sending rewards were used to check for duplicate participation. Cross-sectional studies don’t need a control group as the selected population is not based on exposure. A cross-sectional study is essential when researching the prevailing characteristics in a given population at a single point in time. Cross-sectional studies are often used to analyze demography, financial reports, and election polls. You could also use them in medical research or when building a marketing strategy, for instance.
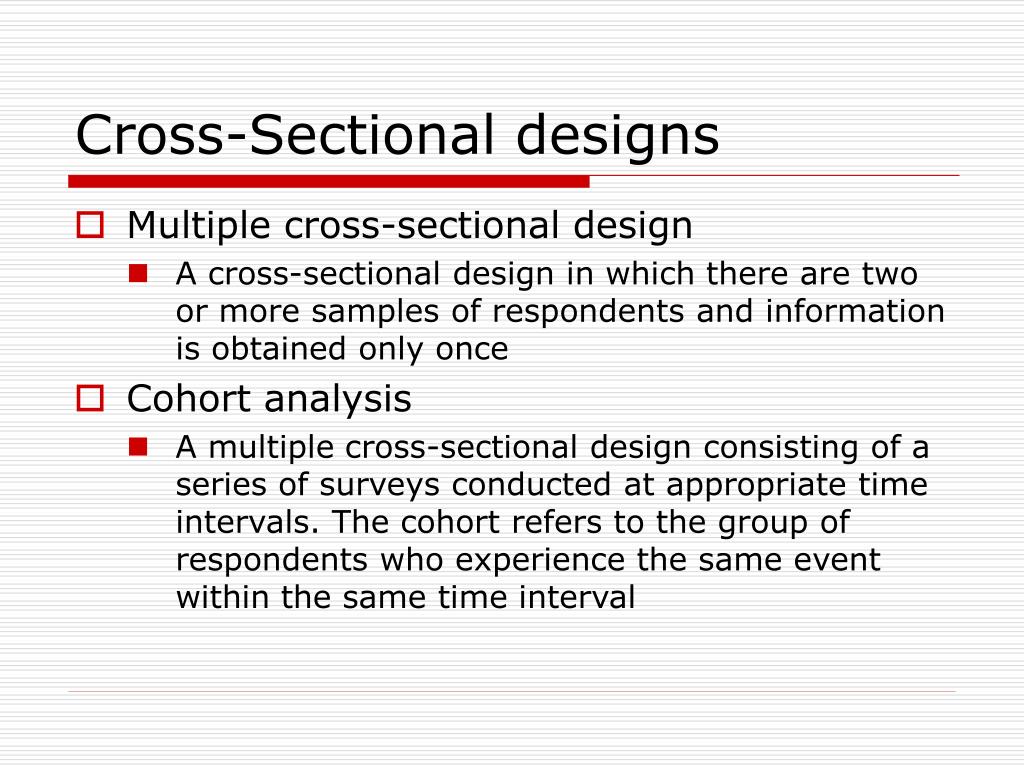
Cross-sectional research differs from longitudinal studies in several important ways. The key difference is that a cross-sectional study is designed to look at a variable at a particular point in time. A longitudinal study evaluates multiple measures over an extended period to detect trends and changes. Researchers can collect data on a few different variables to see how they affect a certain condition. For example, differences in sex, age, educational status, and income might correlate with voting tendencies or give market researchers clues about purchasing habits.

No comments:
Post a Comment